All About Polygons
Discover polygons: learn what a polygon is, the different types of polygons and identify polygons in the real world.

Author
Katie Wickliff
Published:
May 2025
Key takeaways
- • A polygon is a flat shape with straight sides.
- • Polygons can have many sides, which gives the polygon its name.
- • The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360°, regardless of the number of sides.
Our world is filled with polygons, from simple squares, rectangles, and triangles to complex hexagons, octagons, and decagons. Because polygons are everywhere, it’s no surprise that kids as young as kindergarten start learning about these important shapes.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at different types of polygons and their key characteristics and properties. We’ll also discuss the mathematical formulas to calculate the sum of the interior angles, exterior angles, and diagonals, concepts that students will explore in later grades. Plus, we’ll highlight real world examples and share ways to help your child build confidence in geometry. Let’s get started!
What is a polygon?
A polygon is a flat, two-dimensional shape with straight sides. These sides are formed by connecting line segments. It’s important to note that “polygon” refers to a category of shapes, not a single shape. Many shapes are polygons, including triangles, quadrilaterals, and pentagons.
Table of contents
Access more math practice with DreamBox
Turn math into playtime with DreamBox Math
DREAMBOX MATH
Get started for FREE today!

Types of polygons
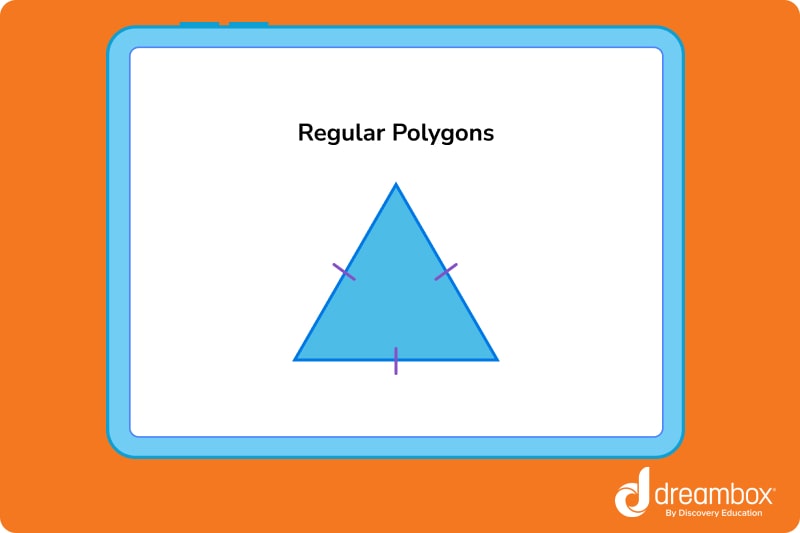
Regular polygons
In a regular polygon shape, all sides are the same length and all angles are equal in measure. One example of a regular polygon is an equilateral triangle.
Irregular polygons
In an irregular polygon, the sides and angles are not all equal. To be an irregular polygon, at least one side or angle must be different from the rest.
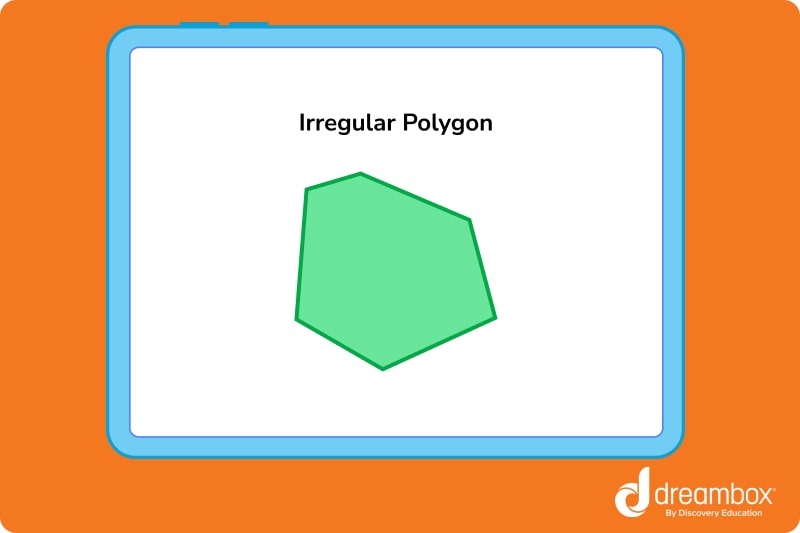
To visualize the difference between a regular and irregular polygon, picture a regular polygon carefully traced using a stencil or template. Each line and angle should be the exact same. Now, imagine an irregular polygon drawn by a kindergartener with a crayon and a blank piece of paper! Very cute, but likely not perfectly balanced.
Convex polygons
For a shape to be considered convex, all of its interior angles must point outward. In other words, every single angle is less than 180°.
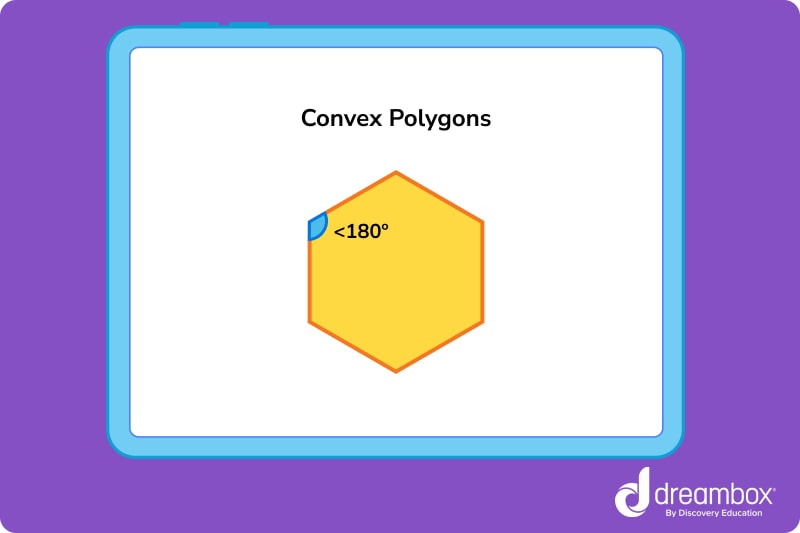
Concave polygons
A concave polygon is one where at least one interior angle “caves in.” In other words, if even just one angle measures greater than 180°, the shape is concave.
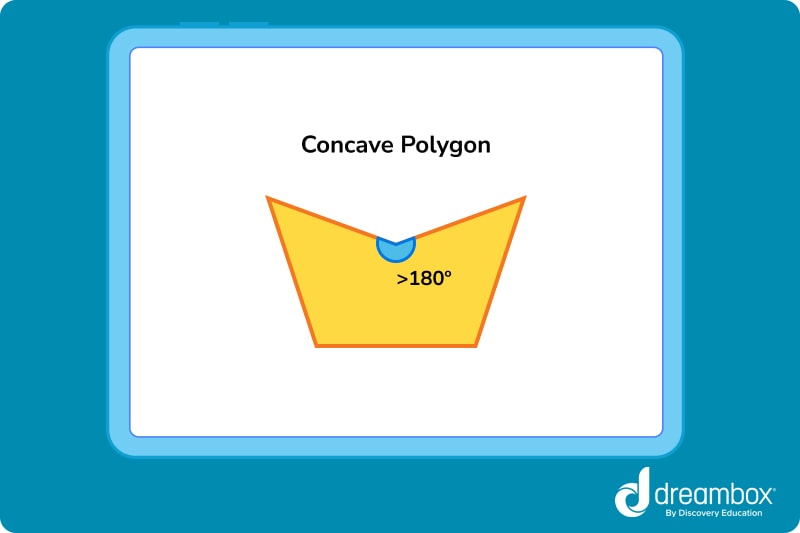
Simple polygon
A simple polygon is flat, neat, and connected from one corner to the next. The sides are closed and non-intersecting, which means they do not crisscross or overlap.
Complex polygon
In a complex polygon, some or all of the sides intersect. Even though the lines may twist, loop, or cross, if the sides are straight and form a closed figure, it’s still a polygon. Complex polygons are likely to show up in more advanced geometry studies.

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
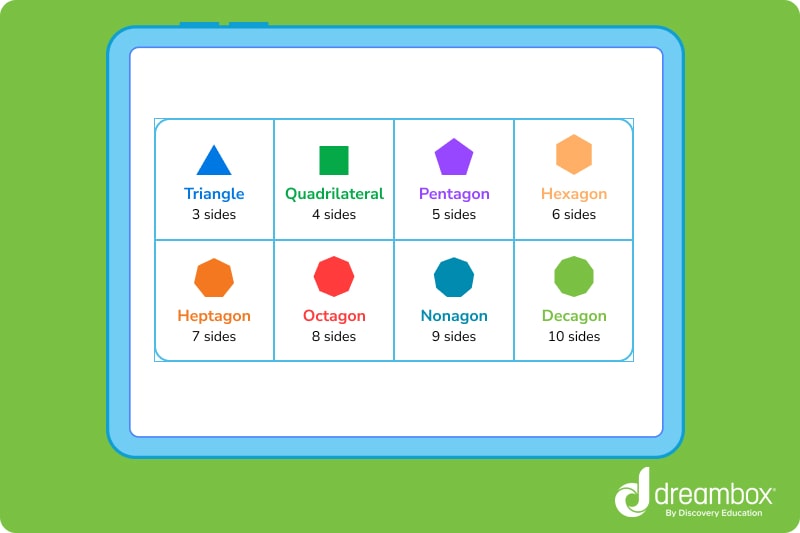
Classification by number of sides
Polygons are also classified by the number of straight sides they have:
Key properties of polygons
No matter the type or number of sides, all polygons share key properties that distinguish them from other shapes. Some of these important features include:
Number of sides, angles and vertices
Every polygon has an equal number of sides, angles, and vertices. For example, a triangle has 3 sides, 3 angles, and 3 vertices, while a square has 4 sides, 4 angles, and 4 vertices.
Sum of interior angles
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon depends on the number of sides. To find the sum of the interior angles:
Sum of Interior Angles = (Number of sides- 2) x 180°
For example, the sum of the interior angles of a pentagon (a 5 sided figure) is:
(5 – 2) × 180° = 540°
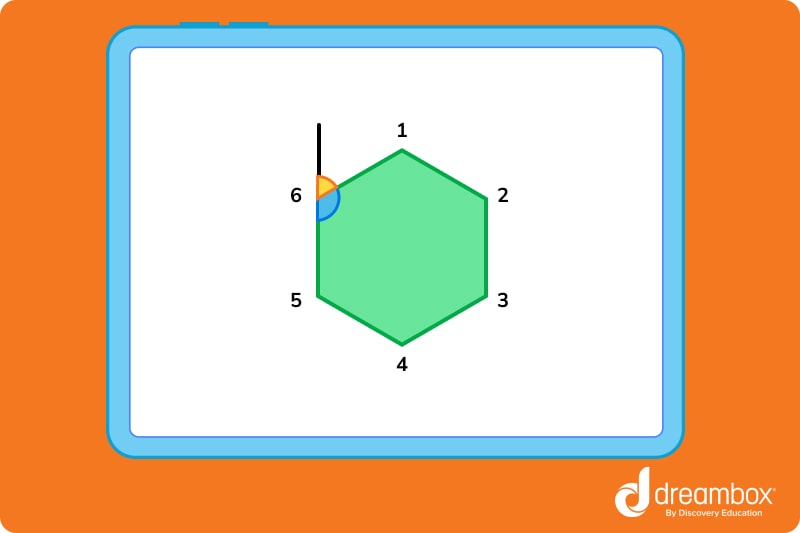
Sum of exterior angles
The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360°, regardless of the number of sides.
To find the measurement of one exterior angle of a regular polygon, use this formula:
One exterior angle = 360 ÷ number of sides
To find the exterior angle of a regular hexagon (a 6 sided figure):
360 ÷ 6 = 60°
Each exterior angle is 60 degrees.
Relationship between interior and exterior angles
The interior and exterior angles of each corner of a polygon form a straight line, which means they always add up to 180°. For example, if a polygon’s interior angle is 120°, then the exterior angle is 60°.
Number of diagonals
A diagonal is a straight line that connects two non-adjacent corners inside a shape. To find out how many diagonals a polygon has, use this formula:
Number of Diagonals = (Number of Sides × (Number of Sides− 3)) ÷ 2
For example, the number of diagonals in an octagon (an 8 sided figure) is:
(8 x (8-3)) ÷ 2 = 20
Polygons in the real world
Polygons are everywhere, making it easy for kids to spot them at school, at home, or outdoors! A fun way to explore polygons is to hunt for them in the kitchen. If your child usually thinks of polygons as something only found on math worksheets or art projects, noticing them in food is a delicious way to bring those shapes to life. Some easy examples include:
Tortilla chips (triangles)
Saltine crackers (squares)
Graham crackers (rectangles)
Pizza slices (triangles, rectangles, or squares)
You can also use geometrical cookie cutters to cut fruit, cheese, or cookies into polygons and study the similarities and differences.
For kids who love architecture and the outdoors, point out that most of the structures around us are made of different types of polygons. For example, windows and doors are often made up of squares and rectangles. Triangles add strength and structure to roofs and bridges, while hexagons can show up in tiles and decorative designs. Even at the playground, kids can find polygons in slides, climbing walls, benches, and path designs.
Practicing with polygons
In addition to the hands-on activities found in the kitchen and outdoors, head over to Dreambox for more polygon practice. This interactive online math program offers students math support and enrichment, all tailored to their unique abilities. With Dreambox, your child can find sample problems to develop their geometry skills and confidence!
FAQs
The first 20 polygons have 3 to 22 sides:
- Triangle (3 sides)
- Quadrilateral (4 sides)
- Pentagon (5 sides)
- Hexagon (6 sides)
- Heptagon (7 sides)
- Octagon (8 sides)
- Nonagon (9 sides)
- Decagon (10 sides)
- Hendecagon (11 sides)
- Dodecagon (12 sides)
- Tridecagon (13 sides)
- Tetradecagon (14 sides)
- Pentadecagon (15 sides)
- Hexadecagon (16 sides)
- Heptadecagon (17 sides)
- Octadecagon (18 sides)
- Enneadecagon (19 sides)
- Icosagon (20 sides)
- Icosihenagon (21 sides)
- Icosidigon (22 sides)
You can identify a polygon as a shape that is flat, closed, and two-dimensional. A polygon has straight sides, which are formed by connecting line segments.
A kid-friendly polygon definition is a flat shape with straight sides that are all connected.
A polygon with 100 sides is called a hectogon.
A polygon with 1,000,000 is called a megagon. The prefix “mega” means 1 million.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.
