What is Transitional Kindergarten?
Transitional kindergarten: what it is, how it differs from traditional kindergarten and a look at the pros and cons of this step in your child’s education.

Author
Katie Wickliff
Published:
June 2025
Key takeaways
- • Transitional kindergarten serves as a bridge between preschool and kindergarten for younger students.
- • Transitional kindergarten originated in California as a way to support students who missed the age cutoff for kindergarten.
- • Slower pace, more emphasis on play, and a modified curriculum are all ways that transitional kindergarten benefits students.
Depending on where you live, you might have come across the term “transitional kindergarten” and wondered what it means and whether it impacts your child. This article will define transitional kindergarten and give a brief overview of how and why it began. We’ll also explain how transitional kindergarten differs from traditional kindergarten and preschool, and discuss some of the advantages and potential drawbacks. We hope you’ll emerge with a better understanding of transitional kindergarten and how it might fit into your child’s early education. Let’s get started!
What is transitional kindergarten?
Transitional kindergarten is often referred to as a bridge between preschool and kindergarten, or the first year of a two-year kindergarten experience. Transitional kindergarten typically follows a modified kindergarten curriculum geared toward younger 5-year-olds, helping them build the academic, social, and emotional skills that they’ll need to thrive in traditional kindergarten and beyond.
The origin of transitional kindergarten
Transitional kindergarten began in California in 2010 after the state changed the kindergarten age cutoff from December 2 to September 1. TK was created to support kids who missed the new cutoff, those turning 5 between September 2 and December 2.
Since then, other states like Michigan, Illinois, and Washington have introduced their own TK programs. While these may differ from California’s model, they all aim to better prepare young children for kindergarten, backed by growing research on the value of early education.
Table of contents
- What is it?
- Versus traditional kindergarten
- Versus preschool
- Pros and cons
- FAQs
Strengthen your math skills with DreamBox
Kindergarten Math Resources
See how DreamBox can help your kindergartener with math.
Kindergarten vs Transitional Kindergarten
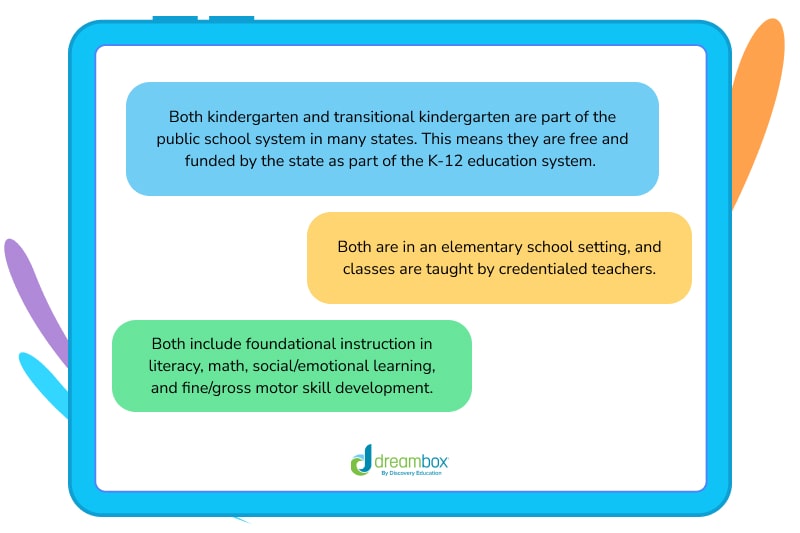
Similarities
Kindergarten and transitional kindergarten are part of the public school system in many states, making them free and state-funded as part of the K-12 education system.
Classes are held in an elementary school setting and taught by credentialed teachers.
Students receive foundational instruction in:
Literacy
Math
Social and emotional learning
Fine and gross motor skill development
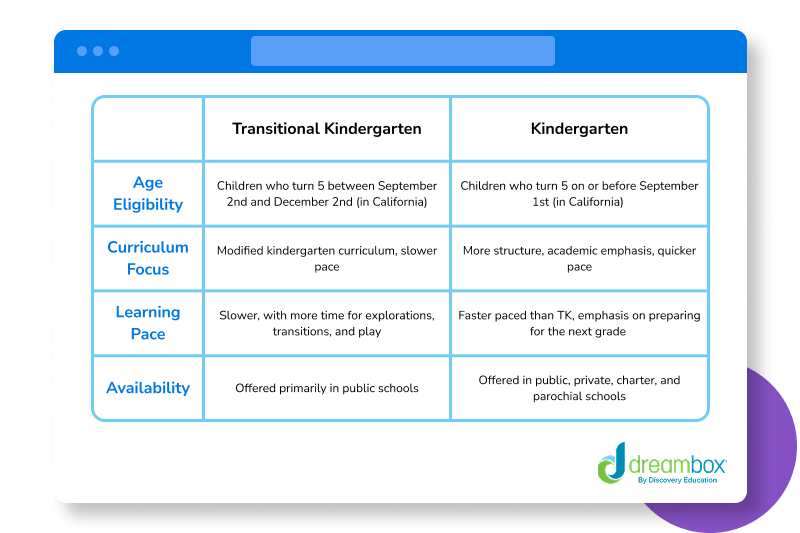
Differences
Age Eligibility (California):
- Transitional Kindergarten (TK): Children who turn 5 between September 2nd and December 2nd
- Kindergarten: Children who turn 5 on or before September 1st
Curriculum Focus:
- TK: Modified kindergarten curriculum, slower pace
- Kindergarten: More structure, academic emphasis, quicker pace
Learning Pace:
- TK: Slower, with more time for explorations, transitions, and play
- Kindergarten: Faster paced than TK, emphasis on preparing for the next grade
Availability:
- TK: Offered primarily in public schools
- Kindergarten: Offered in public, private, charter, and parochial schools
This chart outlines the differences between kindergarten and transitional kindergarten:
Transitional Kindergarten vs Preschool
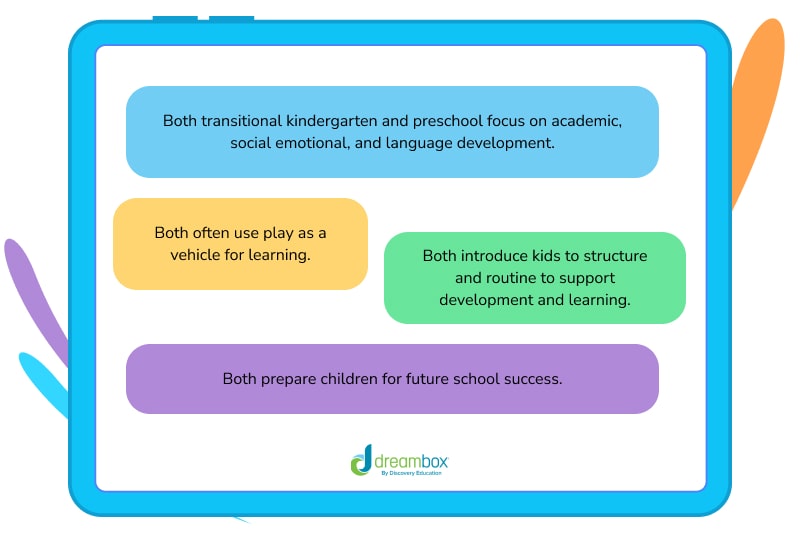
Similarities
- Focus on academic, social-emotional, and language development
- Use play as a vehicle for learning
- Introduce kids to structure and routine to support development and learning
- Prepare children for future school success
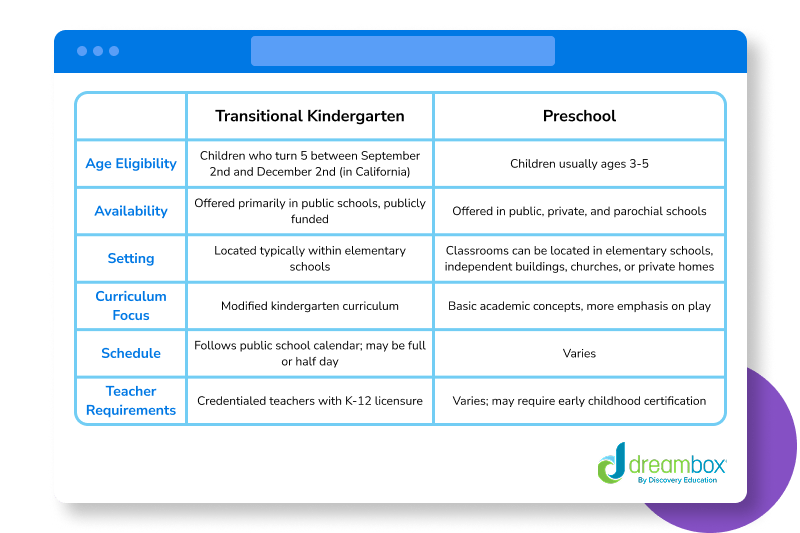
Differences
1. Age Eligibility
- Transitional Kindergarten (TK): Children turning 5 between September 2 – December 2 (specific to California).
- Preschool: Typically for children ages 3 to 5.
2. Availability
- TK: Offered in public schools and is publicly funded.
- Preschool: Available in public, private, and parochial settings.
3. Setting
- TK: Usually located within elementary schools.
- Preschool: Can be in schools, churches, private homes, or independent buildings.
4. Curriculum Focus
- TK: Uses a modified kindergarten curriculum—more structured and academic.
- Preschool: Focuses on basic academics with a strong emphasis on play-based learning.
5. Schedule
- TK: Follows the public school calendar; may be full or half day.
- Preschool: Varies widely—can be part-time, full-time, or flexible depending on the provider.
6. Teacher Requirements
- TK: Teachers must be credentialed K–12 licensed educators.
- Preschool: Requirements vary; may require early childhood education certification, but not always.

The math program that drives results
Get started today!
DreamBox adapts to your child’s level and learning needs, ensuring they are appropriately challenged and get confidence-building wins.
Pros and Cons of Transitional Kindergarten
Pros of Transitional Kindergarten
- Provides a developmentally appropriate bridge between preschool and kindergarten.
- Offers extra time for children to grow academically, socially, and emotionally.
- Uses a modified kindergarten curriculum tailored to younger learners.
- Helps build readiness skills needed for success in kindergarten.
- Taught by fully credentialed elementary teachers.
- Free for families, making it a high-quality and accessible option.
Cons of Transitional Kindergarten
- Not available in all states, check local availability before planning.
- Limited eligibility: Only children with birthdays between September 2 and December 2 qualify (California-specific).
- May exclude children who could benefit but fall outside the age range.
- Some children may be ready for traditional kindergarten and could become disengaged if not challenged enough.
FAQs
Differences between kindergarten and transitional kindergarten include: a modified curriculum, slower pace, and more emphasis on play and exploration. Transitional kindergarten is also for children with a narrow birthday range–from September 2-December 2 in California.
In most cases, children go from transitional kindergarten to kindergarten, not first grade. Transitional kindergarten is designed as a bridge year for students who need more time before entering kindergarten. If your child is experiencing success in transitional kindergarten, try providing them with more enrichment opportunities, such as Dreambox Math. This interactive math program provides kids with fun ways to get the extra challenge (or extra support) that they need to remain excited about school.
Transitional kindergarten is a fantastic idea for many students. It acts as a stepping stone between preschool and kindergarten for younger students, helping them develop the skills they’ll need in kindergarten and beyond.
Take at home math practice to the next level
Empowering parents and educators to make math practice more impactful. Plus, your kids will love it.


About the Author
Katie Wickliff
Katie holds a master’s degree in Education, has over 15 years of education experience as a primary classroom teacher, and is Orton-Gillingham certified tutor. Most importantly, Katie is the mother of two primary school students, ages 8 and 11. She is passionate about maths education and firmly believes that the right tools and support will help every student reach their full potential.